|
Transistor Transistor Logic |
| |
The name refers
to the fact that both input and output of a TTL circuit will
have connection to a transistor.
This not true for RTL (Resistor - Transistor - Logic).
The TTL technology declared
"dead" years ago, but you might still find a few around. During
the 60ies was a TTL family of logic known as the 74-family
developed.
In the 70ies came a new CMOS based family known as the
4000-family - The 74-family and the 4000 are not compatible in
any way (pin or voltage).
A Modern alternative to the
74-family can be found in the 74HC and the 74HCT families.
The HC accept CMOS levels as input, whereas HCT accept TTL
levels as input.
|
Last updated:
27-01-09 |
|
|
|
Basic logic function (gates) |
|
|
|
|
|
Standard TTL Data Book from the 60ies |
|
|
|
|
|
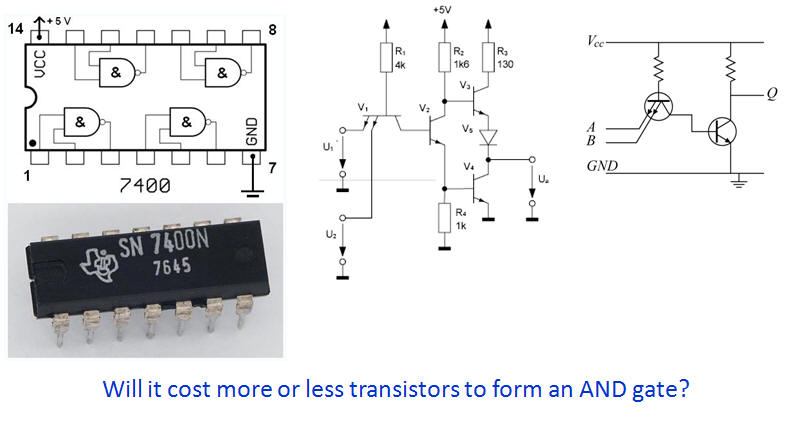
Inside a 7400 – TTL - NAND |
| |
|
The BJT or Bipolar
Junction Transistors was invented in the late
1940ies and started the age of electronic.
You may look at a
BJT as a: Current generator controlled
by a current - meaning the current which
lead into the base will result in a larger collector
current. Ic = hFE * Ib
|
| |
|
| |
 |
|
Drag mouse for
answer: YES - It
will cost you at least one more transistor in order to turn a
NAND gate into a AND gate. This fact was important to have in
mind before the IC became common. All digital circuits was built
with discrete components
|
Why
where NAND gates so popular in the 60ies ?
|
Drag mouse for
answer: Your
able to build all digital logic with only NAND gates - Hence can
a NAND gate be an inverter and the classic AND-OR network can be
replaced by a NAND-NAND.
|
|
|
|
TTL demands current to keep a state 0/1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |