D-Flip/Flop's the most
important sequential memory element which can be found in all
types of programmable logic and hence its used by default in all
types of synchronous designs.
|
|
|
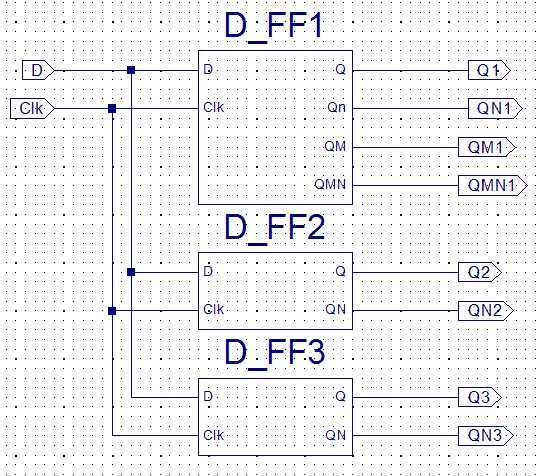
This exercise present 3 different
implementations of D-F/F's. I prefer to use a multiplexer based
D-Latch instead of the more realistic circuit which can be found
in textbooks
A "real-life" D-F/F will normally be based on
three feedback loops or a similar CMOS based circuit.
Study
the D-F/F circuit
here
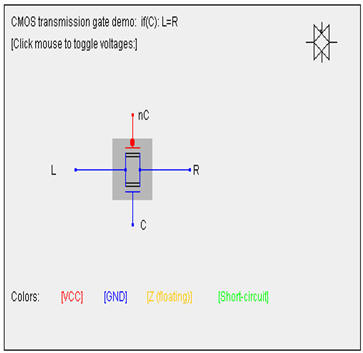
Or the
CMOS D-latch
here
(go to the bottom)
|
|
|
|
|
|
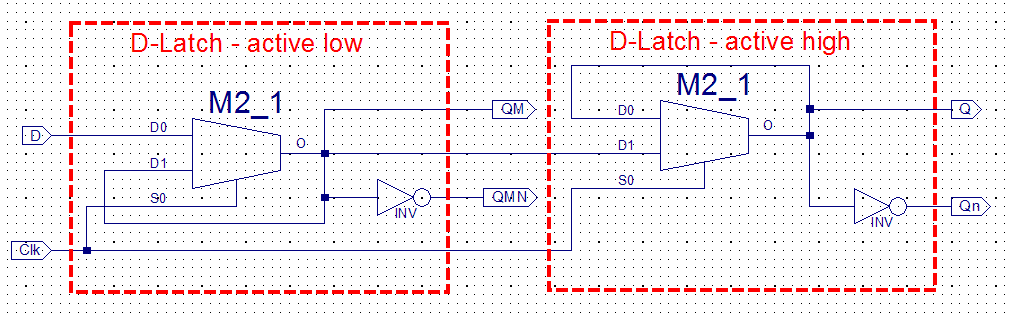 |
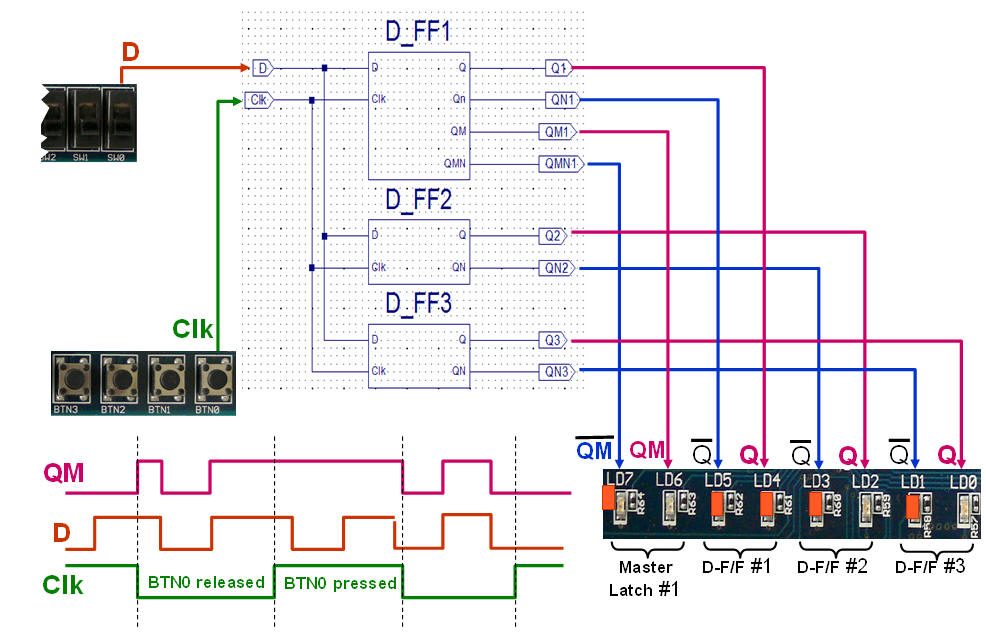
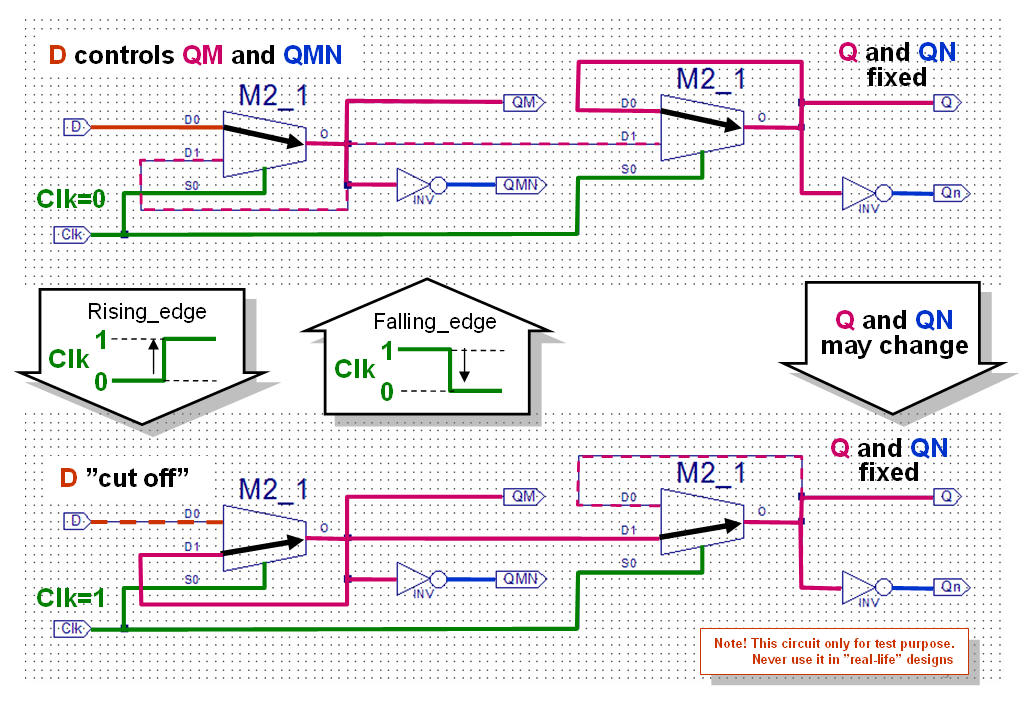
The functionality of a
D-F/F can be obtained by connecting two D-Lathes in series. (See
the explanation below)
One D-Latch should be active low and the another active high.
What happens if the two latches changes places?
Note! The Mux implementation
with D-Latches
not advisable in practice, but nevertheless its works in test.
|
|
|
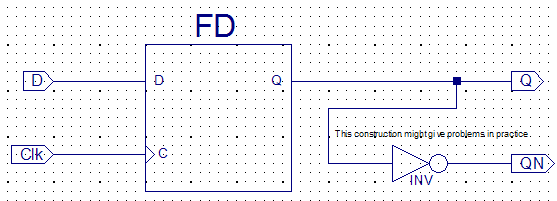
The Schematic symbols
library of ISE offers several versions of D-F/Fs.
Check them out yourself or
learn more in the next exercise.
|
|
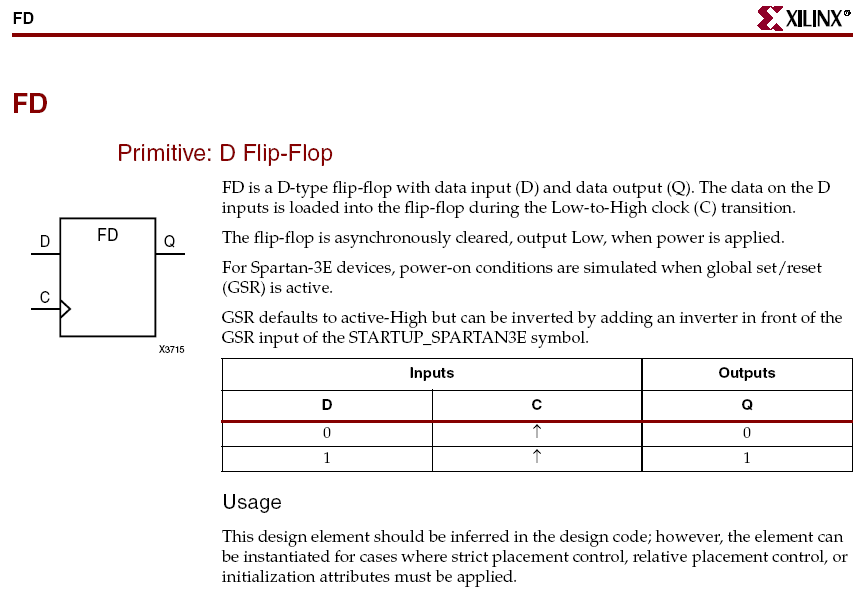
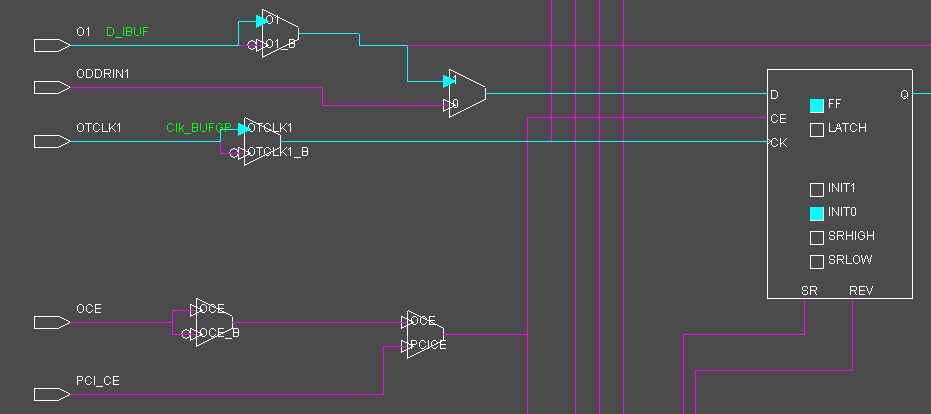
Extract from the Xilinx datasheet of Spartan 3E devices. |
| |
|
|
A VHDL signal can be
connection to a number of Predefined Attributes.
'Event most likely the
only attribute you ever need unless your about write "advanced"
VHDL code.
The predefined functions
Rising_edge( )
and Falling_edge( )
are replacements for the similar 'event
expressions.
Read more about in the
documentations like
Hardi - page 51 or under the Language Templates.
Will the two versions of
D-F/F's used the same number of internal F/F's?
|

|
| |

|
 |
| |
 |
| |
-
Download the
bit-file for testing here: For the BASYS kit use
Test_D_FFs.bit or
NEXYS_test_d_latches.bit
Try it yourself ... the functionality of the different implementations of
D-Flip/Flops.
-
Please note the
output from D-F/F3 after the download of the bit-file.
How come ....... ?
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
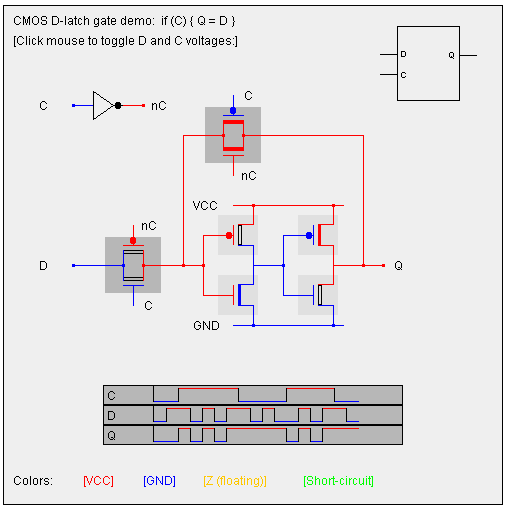 |
Learn more about the CMOS
D-latch
here
(go to the bottom) |
